Introduction to Mount Rinjani
Perched majestically on the island of Lombok, Indonesia, Mount Rinjani is more than just an active volcano; it is a symbol of natural beauty, geological significance, and cultural richness. As the second-highest volcano in Indonesia, Rinjani commands attention with its towering presence, rugged terrains, and lush surrounding landscape. For adventure enthusiasts, nature lovers, and cultural explorers alike, Rinjani offers an unmatched experience that combines breathtaking scenery with a glimpse into the island’s profound natural history. Recognized not only for its geological activity but also for its role in local traditions and ecological diversity, Mount Rinjani stands as a must-visit destination for those seeking an awe-inspiring adventure and deepening connection to Indonesia’s natural heritage.
Location and Geographical Features
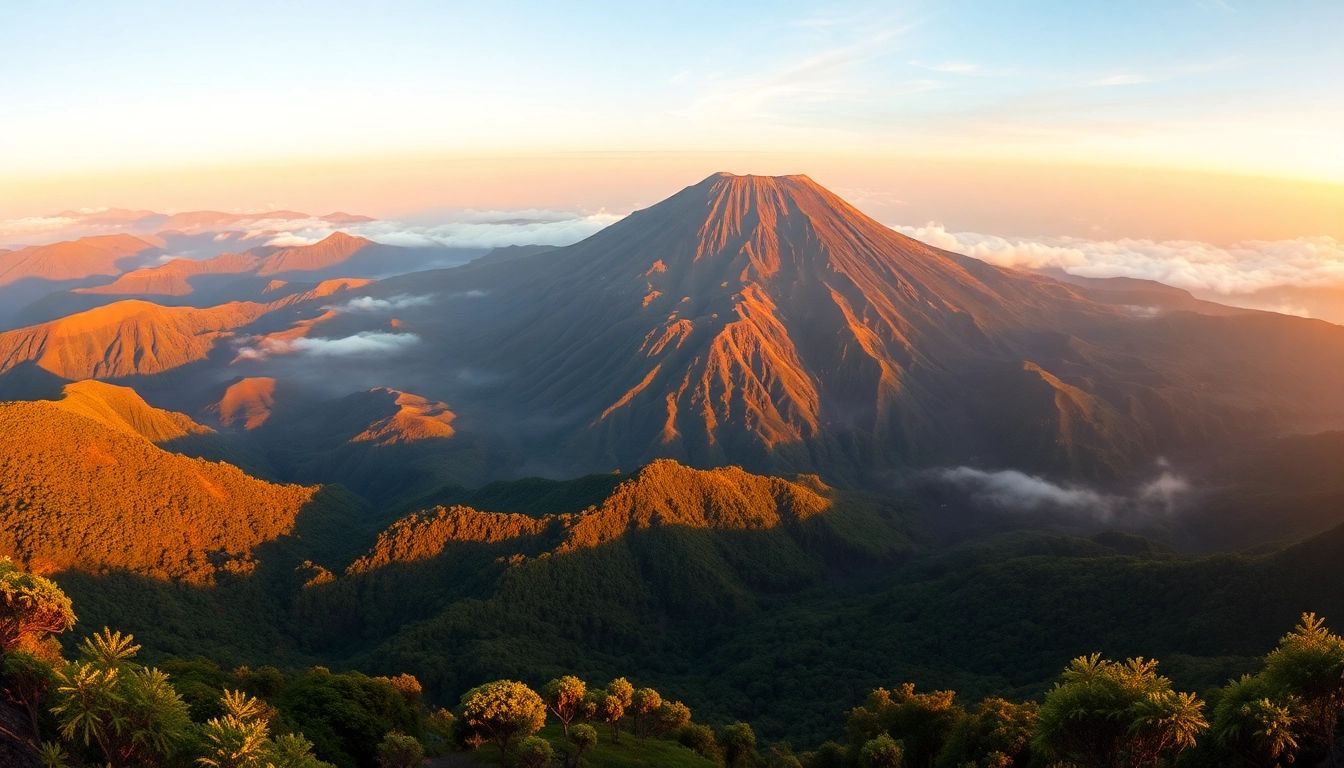
Mount Rinjani is situated in the northern part of Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Its coordinates place it within the boundaries of Gunung Rinjani National Park, a protected area covering approximately 41,330 hectares of diverse ecosystems. Geographically, Rinjani is a stratovolcano, characterized by its broad, complex structure comprising multiple volcanic cones, calderas, and craters. Its elevation reaches 3,726 meters (12,224 feet) above sea level, making it the second-highest volcano in Indonesia and a prominent feature of the region’s topography.
Rinjani’s impressive caldera, approximately 50 square kilometers in size, houses a stunning crater lake called Segara Anak, which translates to “Child of the Sea.” This lake, with its vibrant blue waters, is fed by geothermal springs, hot springs, and volcanic activity, making it a natural wonder. The volcano’s geothermal features include steaming fumaroles and mineral-rich hot springs, which add to the landscape’s surreal quality. The surrounding terrain varies from lush rainforests to semi-dry savannas, supporting rich biodiversity. The mountain’s volcanic activity has shaped the landscape over millennia, creating a rugged terrain that challenges trekkers but rewards them with unrivaled views and raw natural beauty.
Historical Significance and Volcanic Activity
Mount Rinjani’s geological history is deeply intertwined with Indonesia’s volcanic activity, which is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. The volcano’s most notable eruption occurred in 1257, originating from the ancient volcano Samalas, which significantly impacted global climate conditions. The eruption ejected vast ash clouds and pyroclastic flows, causing a period of climate cooling and affecting agricultural productivity in neighboring regions. This historic event illustrates Rinjani’s potential for powerful eruptions and underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and research.
Rinjani remains an active volcano, with periodic eruptions and geothermal activity recorded over recent decades. The last significant eruption was in 2016, which led to temporary restrictions on access for trekkers due to ash emissions. Volcanologists continuously monitor seismic activities, gas emissions, and ground deformation to forecast potential eruptions and ensure visitor safety. Understanding Rinjani’s volatile nature is vital for local authorities, scientists, and tourists, emphasizing the importance of respecting safety protocols and staying informed about volcanic alerts.
Why Mount Rinjani Is a Must-Visit Attraction
Beyond its geological significance, Mount Rinjani captivates visitors with its stunning scenery, cultural significance, and adventure opportunities. Its panoramic vistas of the surrounding islands, ocean, and the crater lake are unparalleled. Trekking to its summit offers a profound sense of achievement, set against the backdrop of sunrise and the expansive Indonesian archipelago.
Additionally, Rinjani’s rich cultural landscape includes local Sasak and Lombok traditions, woven into the experience of the trek and the local hospitality. The mountain also acts as a vital part of the island’s eco-tourism, promoting conservation and sustainable travel practices. For travelers who seek both adventure and cultural immersion, Rinjani provides a diverse spectrum of enriching experiences, making it a top priority on any Indonesia itinerary.
Preparing for a Rinjani Trekking Expedition
Necessary Equipment and Clothing
Preparation is key to a successful and safe Rinjani trekking adventure. Essential gear includes a sturdy hiking backpack, layered clothing suitable for varying temperatures, windproof and waterproof jackets, and thermal wear for cold nights at higher altitudes. Sleeping bags rated for low temperatures, headlamps, and trekking poles are indispensable accessories. Given the volcanic terrain, durable hiking boots with good ankle support help prevent injuries.
Additional safety gear includes masks to protect against ash and dust, gloves, and personal first aid kits. It’s recommended to carry high-energy snacks, water purification tablets, and lightweight, high-protein food supplies. Proper gear not only enhances comfort but also minimizes health risks during the challenging trek.
Best Seasons and Optimal Weather Conditions
The best time to undertake the Rinjani trek is during the dry season, which spans from May to October. During these months, weather conditions are typically clear, with minimal rainfall, and temperatures are manageable. June through August offers the most stable weather, ideal for high-altitude trekking.
Travelers should avoid the rainy season (November to April), when the trails become slippery, and the risk of landslides and volcanic activity increases. Monitoring local weather forecasts is crucial, as sudden storms can pose dangers even during the dry season. Planning your trek during the optimal months ensures safety, better visibility, and an overall more enjoyable experience.
Health and Safety Tips for Trekking
Health preparedness includes vaccinations, if recommended, and carrying necessary medications for altitude sickness, diarrhea, and common ailments. Acclimatization is vital; climbers should spend a day or two in Sembalun or Senaru villages before ascending to adapt to the elevation.
Hydration, nutrition, and adequate rest are crucial to prevent fatigue and altitude-related issues. Awareness of potential dangers, such as volcanic activity, weather changes, and terrain hazards, is essential. Hiring experienced guides can greatly enhance safety, as they are familiar with the route and emergency procedures. Always inform someone about your itinerary, carry communication devices, and follow local authorities’ updates regarding volcanic activity and trail conditions.
Trail Routes and Trekking Guides
Sembalun Lane: The Popularer Path
The Sembalun route stands out as the most popular trekking path due to its relatively gentle slope, stunning scenery, and well-maintained facilities. Starting from Sembalun Village, it offers trekkers a gradual ascent through agricultural landscapes, grasslands, and volcanic terrain. The trail typically takes 2-3 days, with the summit reachable from the crater rim early in the morning.
This route provides spectacular views of the crater lake, surrounding islands, and the sunrise over Lombok. It is suitable for trekkers with moderate fitness levels and provides ample opportunities for photography and wildlife observation. Guided treks are highly recommended, as local guides possess invaluable knowledge about the route, safety, and cultural significance.
Senggigi and Torean Routes
Senggigi and Torean are alternative routes that appeal to more experienced hikers seeking less crowded trails. These paths are more challenging due to steeper inclines and less-developed infrastructure. They offer a sense of adventure and solitude, ideal for seasoned trekkers looking to challenge themselves and experience raw, untouched landscapes.
Proper preparation, local guidance, and rigorous physical training are necessary when choosing these routes. Trekkers should also heed environmental concerns, practicing responsible tourism and minimizing impact.
Hiring Local Guides and Mountain Porters
Engaging certified local guides and porters is crucial for a safe and enriching Rinjani experience. Guides assist with navigation, safety, and sharing cultural insights, enriching the trek with local stories and traditions. Mountain porters can carry supplies and gear, easing the physical burden and allowing trekkers to focus on the journey.
Always choose reputable guiding agencies that adhere to ethical employment practices. Proper remuneration and respect for local communities foster sustainable tourism, supporting livelihoods and preserving traditional knowledge and customs.
Experiencing the Natural Beauty of Rinjani
Highlights: Crater Lake and Hot Springs
The centerpiece of the Rinjani experience is the Segara Anak crater lake, whose shimmering blue waters are framed by volcanic slopes and lush vegetation. Trekkers can enjoy panoramic views, boat trips on the lake, or soak in nearby hot springs, such as the Pusuk Route Hot Springs, which provide relaxing thermal baths amidst stunning scenery.
The hot springs are rich in minerals, believed to have therapeutic properties, offering a perfect way to unwind after a strenuous day. These geothermal features are also indicators of ongoing volcanic activity, reminding visitors of the dynamic Earth processes beneath their feet.
Wildlife and Plant Diversity
Rinjani National Park boasts a rich tapestry of flora and fauna. The lower elevations feature tropical rainforests with species such as ebony trees, orchids, and medicinal plants. Higher up, alpine vegetation and endemic species adapted to volcanic environments thrive.
The park is home to animals like the Javan hawk-eagle,arthropods, and various reptile species. Birdwatchers can spot hornbills, kingfishers, and migratory birds. Preserving this biodiversity is critical, and responsible trekkers contribute to conservation efforts by minimizing their ecological footprint.
Photographic Opportunities and Scenic Viewpoints
Every turn on the trail offers stunning vistas—be it the expansive crater lake, the sunrise from the summit, or panoramic views of Lombok and beyond. Key viewpoints include the Sembalun pass, the summit, and the panoramic terraces near the crater rim. Photographers are encouraged to capture the interplay of light and shadow during dawn and dusk to create evocative images of the landscape.
Post-Trekking and Conservation Efforts
Responsible Tourism and Leave No Trace
Ensuring the preservation of Mount Rinjani’s pristine environment requires responsible tourism practices. Visitors are urged to follow the Leave No Trace principles: packing out all trash, minimizing campfire impacts, respecting wildlife, and staying on established trails. Educational programs and park signage reinforce these values, aiming to reduce environmental degradation caused by trekking activities.
Supporting Local Communities
Tourism revenue is vital for the local economy. Travelers can support community-based initiatives by purchasing local handmade crafts, staying in eco-lodges, and choosing guided tours operated by local residents. Engaging with community enterprises helps sustain traditional livelihoods and promotes cultural exchange, enriching the overall experience while fostering economic resilience.
The Future of Mount Rinjani Preservation
Preservation efforts include ongoing scientific monitoring, environmental education, and sustainable tourism policies. International partnerships aid in conservation projects, such as reforestation, wildlife protection, and volcanic hazard mitigation. Public awareness campaigns highlight the importance of ecological balance, ensuring that future generations can enjoy Rinjani’s natural splendor.